is co2 a polar molecule Is carbon dioxide (co2) polar or nonpolar? » science abc
As we look at our planet from afar, it may seem that all the molecules in the air around us are the same. But in reality, there are different types of molecules that make up the air we breathe, and their composition has a significant impact on our environment. Today, we’re going to focus on one of the most important molecules in our atmosphere: CO2. CO2, or carbon dioxide, is a molecule made up of one carbon atom and two oxygen atoms. It may seem simple, but this molecule is a crucial component of the Earth’s atmosphere. It plays an essential role in the planet’s natural carbon cycle, which helps regulate the Earth’s temperature and supports the growth of plants and trees. One of the main reasons CO2 is so crucial is that it is a greenhouse gas. This means that it traps heat from the sun that would otherwise escape into space, creating a warming effect that helps regulate the temperature of our planet. However, when there is too much CO2 in the atmosphere, it can lead to a phenomenon known as global warming, where the Earth’s temperature steadily rises over time. To understand why CO2 is a greenhouse gas, we need to look at its molecular structure. CO2 is a linear molecule, meaning the two oxygen atoms are directly bonded to the carbon atom, forming an angle of 180 degrees. Due to this arrangement, the molecule has a dipole moment, which makes it polar. This polarity means that the CO2 molecule can absorb and emit infrared radiation, which is one of the key components of the greenhouse effect. When we burn fossil fuels, such as coal, oil, and natural gas, we release CO2 into the atmosphere. This is because these fuels are made up of carbon and hydrogen, and when we burn them, we react carbon with oxygen from the air to produce CO2. The more fossil fuels we burn, the more CO2 we produce, and the more we contribute to global warming. It’s important to note that CO2 isn’t the only greenhouse gas. Methane, water vapor, and other gases also contribute to the greenhouse effect. However, CO2 is the most significant contributor because of the sheer amount of it that we release into the atmosphere each year. To put this into perspective, humans have increased the amount of CO2 in the atmosphere by around 45% since the Industrial Revolution. Now that we understand how CO2 contributes to the greenhouse effect, let’s take a closer look at the two images in this post. The first image shows the molecular structure of CO2. As we discussed earlier, the molecule is linear, with a carbon atom in the center and two oxygen atoms on either side. This structure allows the molecule to be polar and absorb infrared radiation. The second image shows the impact of climate change on our planet, particularly how rising temperatures are melting Arctic ice. This melting can lead to a rise in sea levels, which can have a significant impact on coastal areas and their populations. This image is a stark reminder of the fact that climate change is not a distant threat but an immediate and real one. In summary, CO2 may seem like an insignificant molecule, but it plays a crucial role in regulating the temperature of our planet. However, when we release too much CO2 into the atmosphere, it can lead to global warming and other disastrous consequences. It’s important that we all work together to reduce our carbon footprint and ensure a sustainable future for our planet.
If you are searching about Is Carbon Dioxide (CO2) Polar Or Nonpolar? » Science ABC you’ve visit to the right page. We have 5 Pictures about Is Carbon Dioxide (CO2) Polar Or Nonpolar? » Science ABC like Is Carbon Dioxide (CO2) Polar Or Nonpolar? » Science ABC, Is CO2 Polar or Nonpolar? - Techiescientist and also Is Carbon Dioxide (CO2) Polar Or Nonpolar? » Science ABC. Here you go:
Is Carbon Dioxide (CO2) Polar Or Nonpolar? » Science ABC
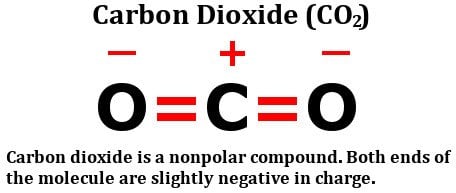 www.scienceabc.comcarbon dioxide co2 polar nonpolar structure bonds molecule bond look combined considered effect must let then these
www.scienceabc.comcarbon dioxide co2 polar nonpolar structure bonds molecule bond look combined considered effect must let then these
Why Is Water A Polar Molecule « Anhourofchemaday
 anhourofchemaday.wordpress.compolar co2 molecule non why water nonpolar oxygen molecular shape if example bent cancel dipole hydrogen direction electronegative than however
anhourofchemaday.wordpress.compolar co2 molecule non why water nonpolar oxygen molecular shape if example bent cancel dipole hydrogen direction electronegative than however
Is Carbon Dioxide (CO2) Polar Or Nonpolar? » Science ABC
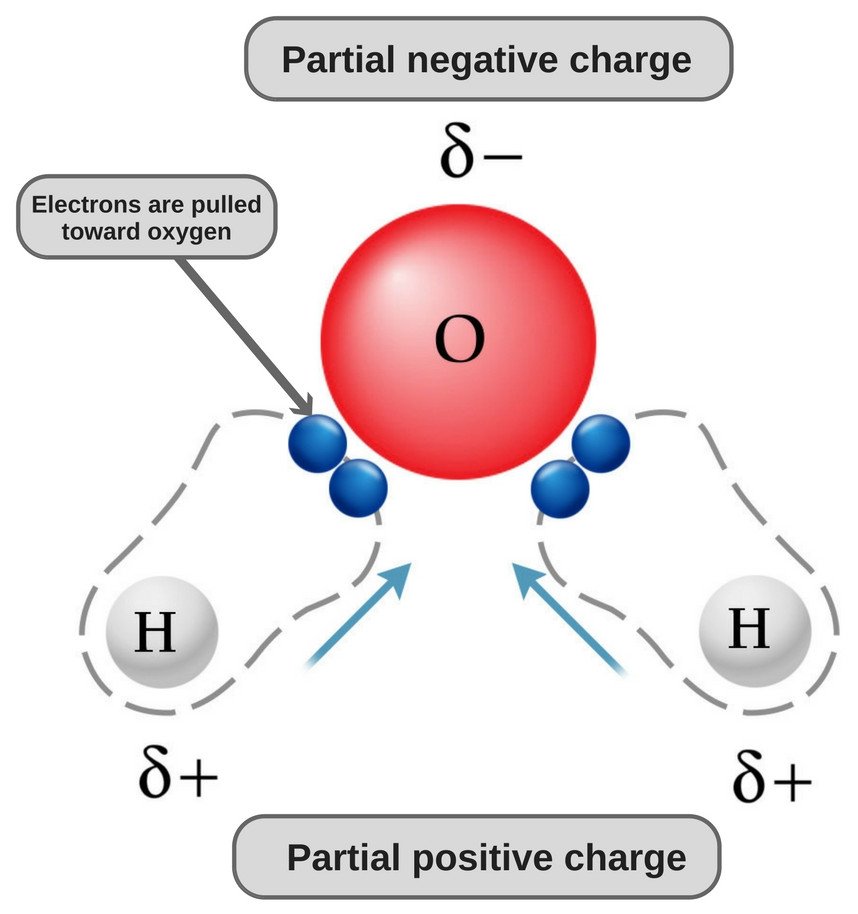 www.scienceabc.compolar molecule water nonpolar co2 carbon dioxide charge positive negative polarity partial oxygen hydrogen why bonds atoms than region abc
www.scienceabc.compolar molecule water nonpolar co2 carbon dioxide charge positive negative polarity partial oxygen hydrogen why bonds atoms than region abc
Is CO2 Polar Or Nonpolar? - Techiescientist
 techiescientist.comdioxide molecule carbone polar dioxyde nonpolar dipole molécule chimicamo atome miscela atomes molecules polarity orbital hybridization linéaire techiescientist oxygène nitrogen
techiescientist.comdioxide molecule carbone polar dioxyde nonpolar dipole molécule chimicamo atome miscela atomes molecules polarity orbital hybridization linéaire techiescientist oxygène nitrogen
Co2 Molecule / Geo Expro Recent Advances In Climate Change Research
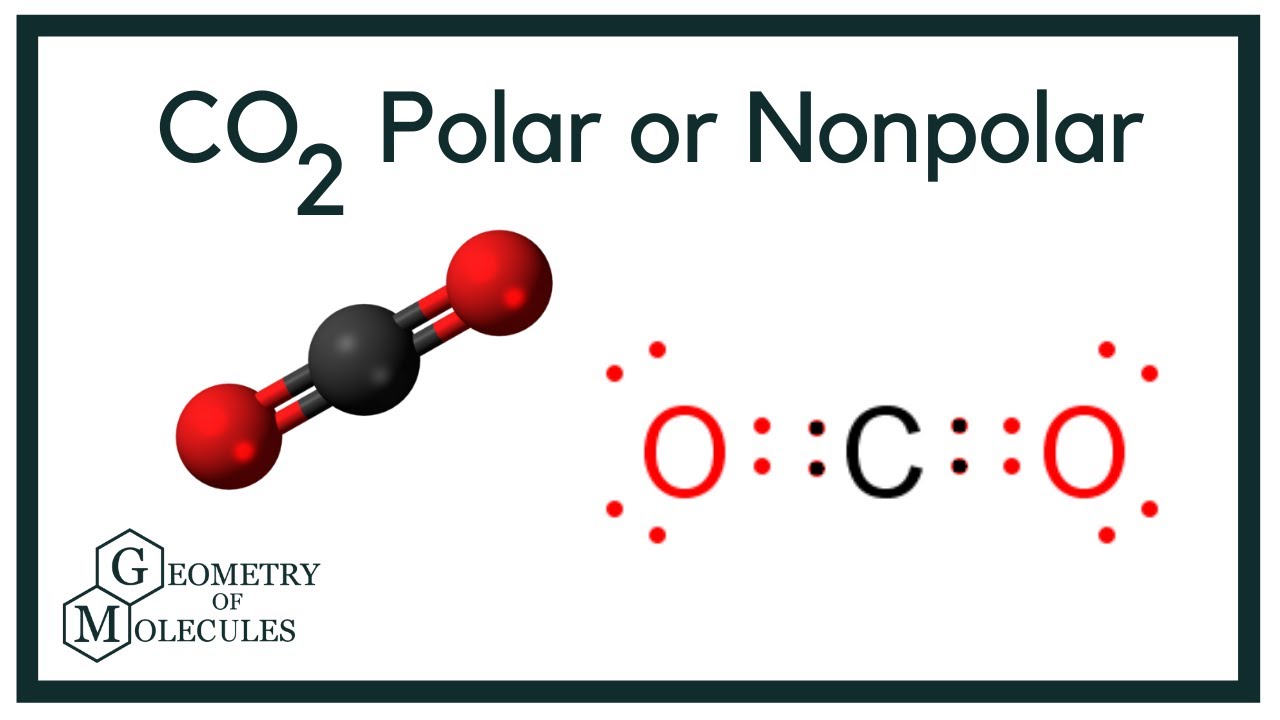 cikaardianti5754.blogspot.comco2 dioxide nonpolar molecule atoms molecules
cikaardianti5754.blogspot.comco2 dioxide nonpolar molecule atoms molecules
Co2 dioxide nonpolar molecule atoms molecules. Why is water a polar molecule « anhourofchemaday. Is co2 polar or nonpolar?